
We are conducting an internal Inventory count: April 24th – 30th. All orders placed after April 22nd will be processed the week of May 1st. More info
Recent Posts



Upcoming Events
Latest Comments
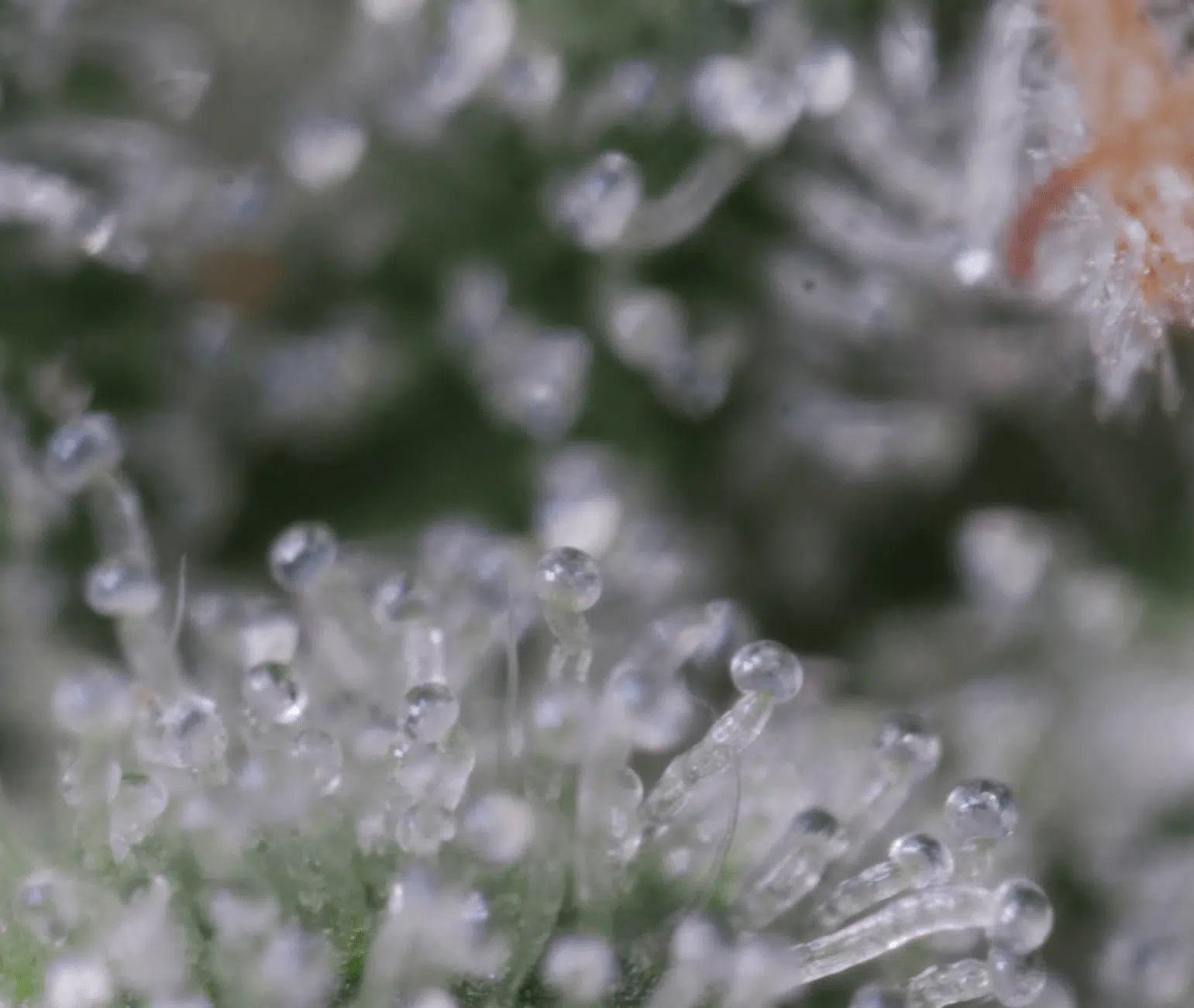
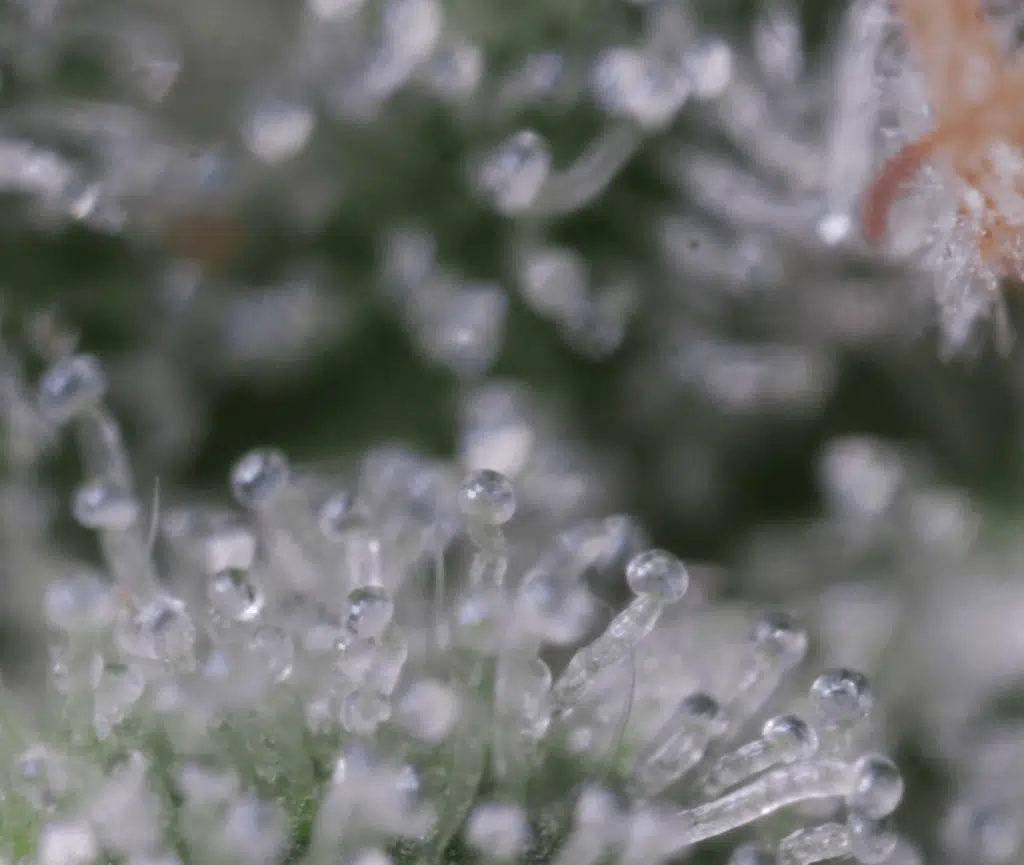


When it comes to cannabis, experienced growers prefer quality over quantity. The truth is, growers today want to produce bigger trichomes, not flowers. Unlike its flowers, cannabis trichomes hold a wealth of psychoactive, medicinal, and therapeutic properties. The market’s changed; instead of gigantic, dull cannabis buds, growers are far more interested in producing tight flowers, covered with a dense layer of crystalized trichomes.
Trichomes are small, dome-like glands that coat the leaves and buds of mature cannabis plants. They are resinous and oily, but also have a glass, or crystal-like appearance. Trichomes also have functional properties. For example, experts argue that trichomes can mitigate leaf and flower temperature, leading to a stronger plant that’s more resistant to bouts of extreme heat or cold (Wagner, 1991).
Also, the hair-like structure of resin glands leads professionals to believe that trichomes can act as a pest-deterrent and defence mechanism via their oily nature and the production of chemical compounds (Wagner, 1991). Fruits, vegetables, and flowers produce trichomes across the plant kingdom. However, specific glands in cannabis have been praised for their unique psychoactive and medicinal compounds.
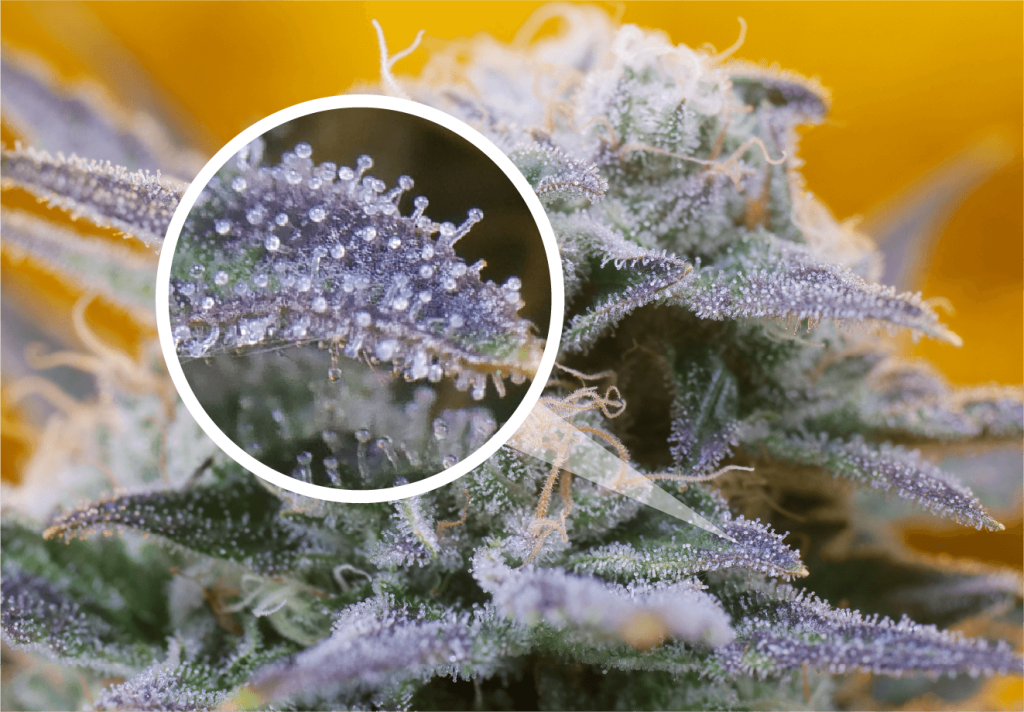

Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the primary psychoactive compound found in cannabis. While perhaps the most prevalent, THC is one of at least 113 cannabinoids found in marijuana plant tissue. THC forms heavily in the lipid glands of exposed plant matter like flowers and leaves as an evolutionary defence response to stress, pests, and environmental conditions.
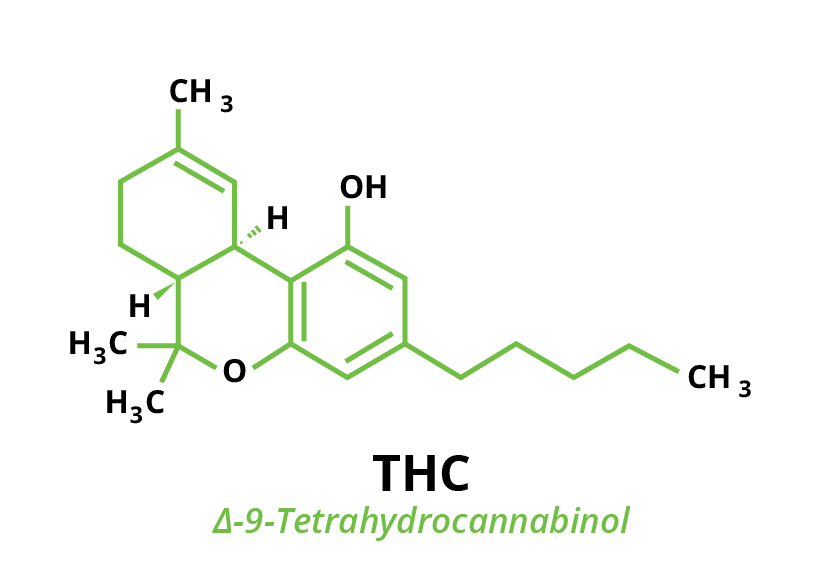
When taken, tetrahydrocannabinol is absorbed into the bloodstream and travels to the brain, attaching itself to the naturally-occurring endocannabinoid receptors located in the brain. This attachment can distort and affect perception, pleasure, thinking, coordination, and movement. In short, THC is the compound in cannabis responsible for making the user feel “high”. However, there are also medicinal and therapeutic uses for THC. For instance, THC has had success in treating pain, discomfort, and bladder overactivity for people with multiple sclerosis.
Cannabidiol or CBD is another immensely important compound found abundantly in cannabis. Also a primary active ingredient in hemp, CBD has been championed widely for its therapeutic and medicinal benefits. And unlike THC, CBD does not cause a “high” when ingested. Potential medicinal benefits are as follows: insomnia relief, acute and chronic pain assistance, inflammation ease, depression support, and arthritis aid (Perez, 2021, para. 1).
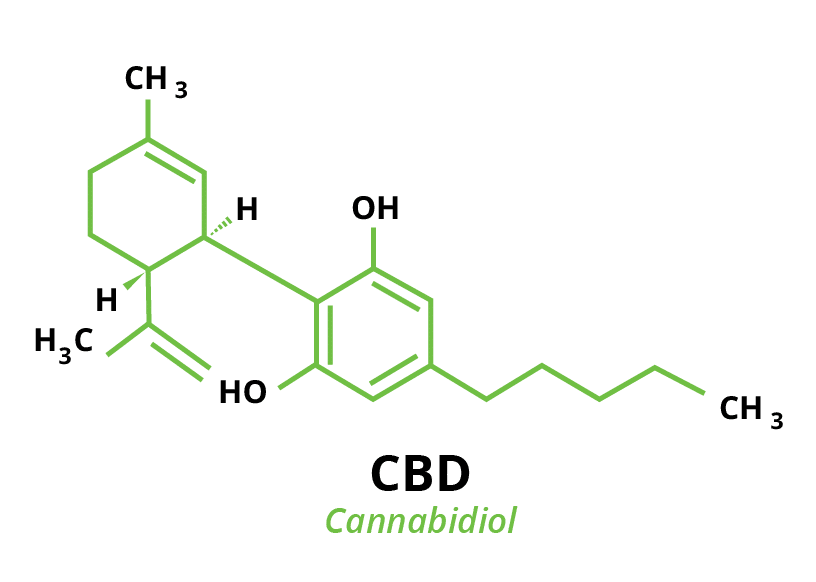
CBD can be ingested in many forms, including oils, herbs, patches, capsules, lotions, sprays, and even bath bombs. Since CBD is a therapeutic compound without any psychoactive effects, individuals using or prescribed CBD may experience a more relaxed and regulated mood, reduced muscle pain, and low fatigue.
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), the precursor of THC, is also found in the resinous glands of cannabis plants. Unlike the smaller molecular compound THC, THCA’s chemical composition is too large to fit into the endocannabinoid receptors in the brain, making it a non-intoxicating active ingredient. In order for a cannabinoid compound to become intoxicating (like THC), the molecule must be small enough to attach itself to a type-1 cannabinoid receptor (CB1). The shape and size of the THCA molecule, however, is too large to make this CB1 to cannabinoid connection.
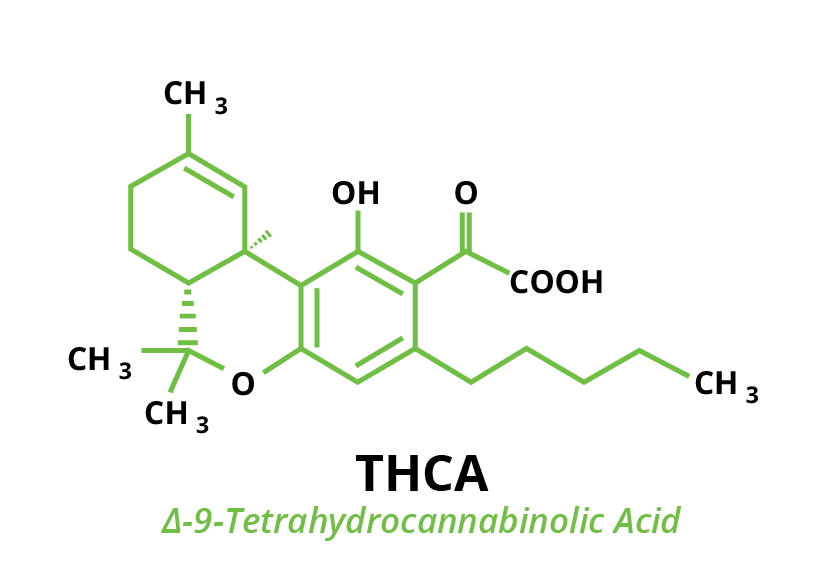
Remember, THCA is the precursor to the intoxicating compound THC. The chemical conversion comes from a simple process called decarboxylation, or the rapid application of heat and light. Heat removes the carboxylic acid group from THCA, altering the THC chemical structure. This makes it the perfect shape to fit into the endocannabinoid system. But like other compounds found in trichomes, THCA alone has amazing health benefits. For example, recent studies have shown that THCA can promote dietary and immune system recovery and function (Ruhaak, 2011).
Cannabinol (CBN) comes from the breakdown of THC in mature cannabis plants. CBN isn’t as psychoactive as THC, but it can still produce a calming, therapeutic effect after consumption. Since CBN doesn’t necessarily produce a “high”, it’s often overlooked as an unimportant cannabinoid. However, there are several benefits of CBN being examined in recent studies. For instance, studies have shown that concentrations of CBN have antibacterial, neuroprotectant, and anti-inflammatory properties. Cannabinol also has a minor sedative effect, leading researchers to believe that future studies will yield further medicinal evidence for the use of CBN.
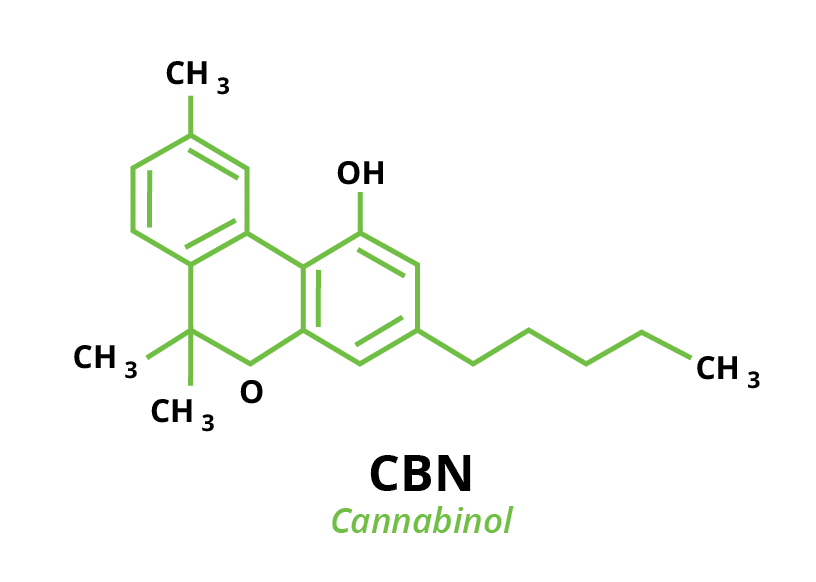
What’s most interesting about CBN is its interaction with other cannabinoids. Dr. Ethan Russo, a neurologist responsible for popularizing the “entourage effect”, says CBN itself isn’t a sedative (Rahn, 2020, para. 5). But when combined with other cannabinoids like THC and CBD, cannabinol can work synergistically to influence certain therapeutic effects.
Cannabis buds are valued on much more than size – strain, terpene concentration and cannabinoid content all play an essential role in determining the value of raw flower. But how do we grow trichomes?
Bring fire to your crop with Rezin, our trichome, flavour, and aroma enhancer. Formulated with trace amounts of molybdenum and vitamin B1, Rezin can be used in both the flowering and flushing periods of growth to boost essential oil, trichome, and resin content.
Rezin contains no plant growth regulators (PGRs), artificial colouring, or dyes. And, since it contains only a trace amount of a single micronutrient, Rezin will not impact the EC/PPM of your nutrient solution. Rezin will help promote aromas and flavours to bring out the best qualities of your plants in both the late-stage and flushing period.
Rezin is the answer to ensure your flowers are covered in beautiful, frosty trichomes.
Remember, to enhance the smell and taste of cannabis, grow trichomes, not flowers! For more information on the products or information mentioned in this article, contact your GreenPlanet representative directly, or your local garden supply store.
GROWERS
LEGAL
CONSUMER
ABOUT
CONNECT
NEWSLETTER
Monday: 8am – 4:30pm
Tuesday: 8am – 4:30pm
Wednesday: 8am – 4:30pm
Thursday: 8am – 4:30pm
Friday: 8am – 4:30pm
Saturday: Closed
Sunday: Closed
Week of Dec 18-22- Regular operating hours
Dec 25- Closed (Stat Holiday)
Dec 26- Closed (Non-Stat day off with pay)
Dec 27-29- Regular operating hours
Jan 1- Closed (Stat Holiday)
Jan 2-5- Regular operating hours
Recent Comments